 |
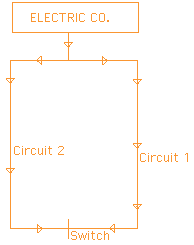
What
does a circuit look like? At the left is a sample diagram of circuits. Lines and arrows indicate the direction and flow of electricity. |
Electric circuits
Electricity follows a path. The path
that an electrical current follows is called an electric circuit.
An electric circuit can be closed or open.
Different buildings and electrical equipment have separate circuits; the flow of electricity can be cut off or changed through switches, usually at the beginning and end of circuits.
 |
What
does a circuit look like? At the left is a sample diagram of circuits. Lines and arrows indicate the direction and flow of electricity. |
Where examples of circuits
can be found.
Circuits are found in many places throughout the world. In your
home, for example, separate circuits are established to control
specific devices and appliances. Circuits are present throughout
the community.
Local electricity companies establish circuits to send specific amounts of electricity to certain regions.
Circuits can also be found on moving objects. Electrical circuits can be found in cars, planes, and other forms of transportation that use electrical energy. Toys can also have electrical circuits; any battery powered toy has electrical circuits.
Series circuits
In series circuits there
is only one path for the electricity to follow. Whenever one thing
in a series circuit stops working, everything in the circuit stops
working. The electricity cannot get past the open part of the
circuit. Series circuits are mostly used for one bell, or one
light bulb, or one motor. Christmas lights are often wired in
a series...if one goes out, all the lights go out.
 |
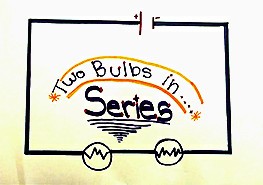 |
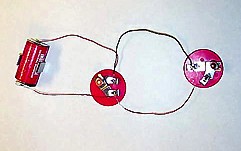
| Two batteries in a series (Sixth Grade project). | Schematic of two light bulbs in a series (Sixth grade project). |
Parallel circuits
A circuit the has more than one path for the electrical current to follow is called a parallel circuit. Each room in a building may be part of a large parallel circuit. All the lights in a room are separate parts of the circuit. The electrical current has many different paths to follow. If one part of the circuit is open, the rest stay closed. If one light bulb burns out, the rest stay lit.
 |
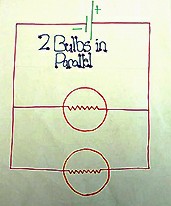 |
| Bulbs in parallel circuit (Sixth grade project). | Schematic of two bulbs in parallel circuit (Sixth grade project). |
If you need more information about electrical circuits and electricity in general, connect to the WWW link : http://www.ibiblio.org/kuphaldt/ for a very complete lesson on electric circuits.
| CIRCUITS & CURRENT HOME PAGE | CIRCUIT BASICS | CIRCUITS IN PERKASIE | MEASURING ELECTRICAL CURRENT |
| ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE | RESISTANCE | KILOWATT | ELECTRIC BILLS |